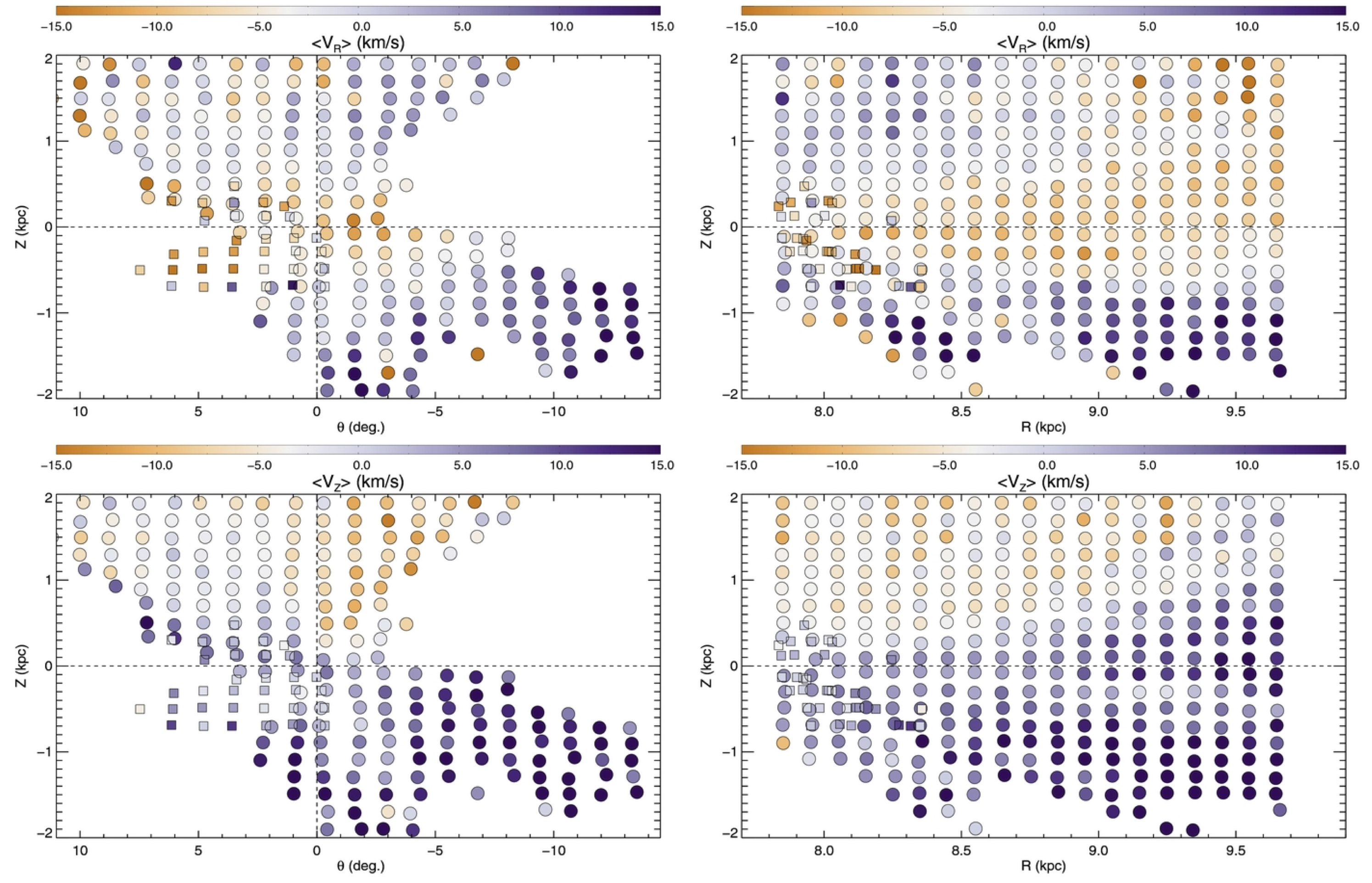
 Radial ($V_{\rm R}$, upper panels) and vertical ($V_{\rm Z}$, lower panels) components of the Galactocentric velocities of stars between $7.8 < R_{\rm GC} < 9.8$ kpc as a function of positions in Z and θ (left column) and Z, R (right column). Circles denote LAMOST data, and small squares are derived from RAVE velocities. Each colored point represents the mean value of all stars within a bin 200 pc wide in R and Z, and 13 in θ. All bins contain at least 50 stars, and some contain many thousands of stars. The dots are centered at the mean position of the stars within each subsample, and color encodes the mean $V_{\rm R}$ or $V_{\rm Z}$ according to the scale given by the color bar at the top. Apparent radial features in the right panels are artifacts consistent with ~20%–30% errors in the distances.
Radial ($V_{\rm R}$, upper panels) and vertical ($V_{\rm Z}$, lower panels) components of the Galactocentric velocities of stars between $7.8 < R_{\rm GC} < 9.8$ kpc as a function of positions in Z and θ (left column) and Z, R (right column). Circles denote LAMOST data, and small squares are derived from RAVE velocities. Each colored point represents the mean value of all stars within a bin 200 pc wide in R and Z, and 13 in θ. All bins contain at least 50 stars, and some contain many thousands of stars. The dots are centered at the mean position of the stars within each subsample, and color encodes the mean $V_{\rm R}$ or $V_{\rm Z}$ according to the scale given by the color bar at the top. Apparent radial features in the right panels are artifacts consistent with ~20%–30% errors in the distances.
Substructure in Bulk Velocities of Milky Way Disk Stars
Abstract
We find that Galactic disk stars near the anticenter exhibit velocity asymmetries in both the Galactocentric radial and vertical components across the midplane as well as azimuthally. These findings are based on Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) spectroscopic velocities for a sample of ~400,000 F-type stars, combined with proper motions from the PPMXL catalog for which we have derived corrections to the zero points based in part on spectroscopically discovered galaxies and QSOs from LAMOST. In the region within 2 kpc outside the Sun’s radius and ±2 kpc from the Galactic midplane, we show that stars above the plane exhibit net outward radial motions with downward vertical velocities, while stars below the plane have roughly the opposite behavior. We discuss this in the context of other recent findings, and conclude that we are likely seeing the signature of vertical disturbances to the disk due to an external perturbation.