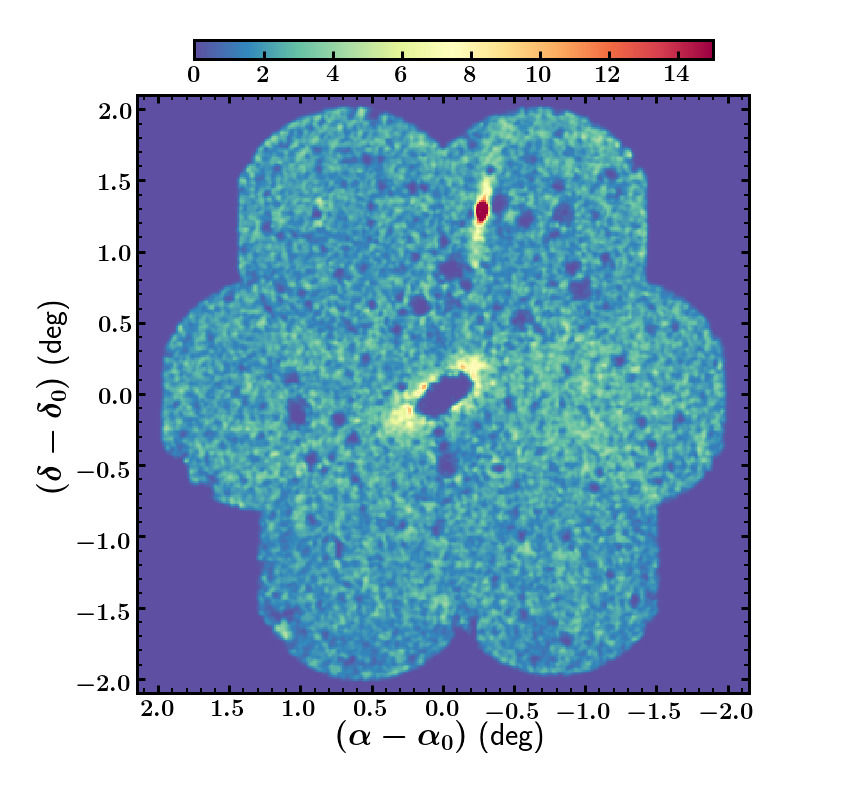
 Density map of red giant branch (RGB) stars around NGC 2403. The field is relatively uniform (other than the holes where nearby bright stars obscure the background objects), except for the extended (red colored) overdensity near the top of the figure. This is the dwarf spheroidal galaxy DDO 44, which we find to be tidally disrupting to form the streams that can be seen extending from the galaxy in both directions.
Density map of red giant branch (RGB) stars around NGC 2403. The field is relatively uniform (other than the holes where nearby bright stars obscure the background objects), except for the extended (red colored) overdensity near the top of the figure. This is the dwarf spheroidal galaxy DDO 44, which we find to be tidally disrupting to form the streams that can be seen extending from the galaxy in both directions.
Tidal destruction in a low mass galaxy environment: the discovery of tidal tails around DDO 44
Abstract
We report the discovery of a $>1$ degree ($\sim$50 kpc) long stellar tidal stream emanating from the dwarf galaxy DDO 44, a likely satellite of Local Volume galaxy NGC 2403 located $\sim$70 kpc in projection from its companion. NGC 2403 is a roughly Large Magellanic Cloud stellar-mass galaxy 3 Mpc away, residing at the outer limits of the M 81 group. We are mapping a large region around NGC 2403 as part of our MADCASH (Magellanic Analogs’ Dwarf Companions and Stellar Halos) survey, reaching point source depths (90% completeness) of (g, i) = (26.5, 26.2). Density maps of old, metal-poor RGB stars reveal tidal streams extending on two sides of DDO 44, with the streams directed toward NGC 2403. We estimate total luminosities of the original DDO 44 system (dwarf and streams combined) to be $M_{i, \rm{tot}} = −13.4$ and $M_{g, \rm{tot}} = −12.6$, with $\sim$25−30% of the luminosity in the streams. Analogs of roughly LMC-mass hosts with massive tidally disrupting satellites are rare in the Illustris simulations, especially at large separations such as that of DDO 44. The few analogs that are present in the models suggest that even low-mass hosts can efficiently quench their massive satellites.